Building Blocks of Project Management: Tools and Techniques
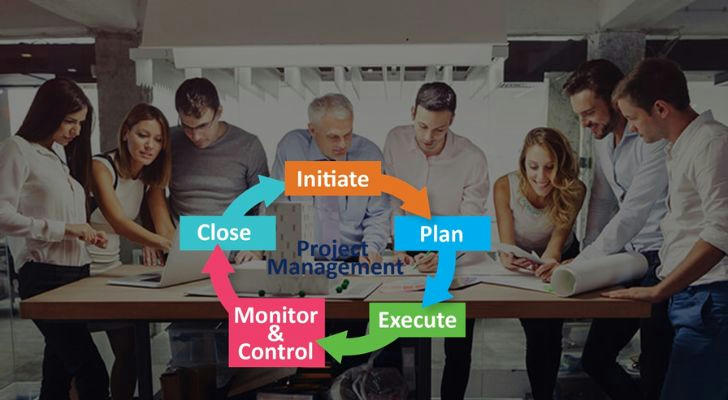
Project management is a complex discipline that requires a combination of various tools and techniques to ensure the successful completion of projects. These building blocks serve as the foundation for effective planning, execution, monitoring, and control of projects.

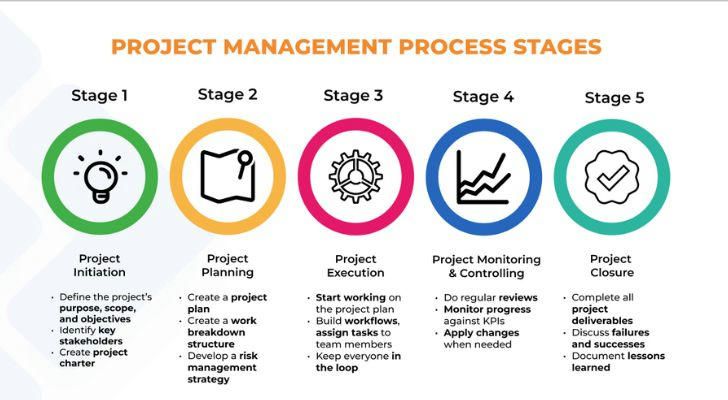
I. Planning Tools and Techniques
A. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
The WBS is a hierarchical decomposition of the project scope into smaller, more manageable components. It breaks down the overall project into work packages, which are the smallest units of work that can be assigned and managed.
For example, in a software development project, the WBS might start with high-level categories such as requirements gathering, design, development, testing, and deployment.
Each of these categories can then be further broken down into more detailed tasks. This tool helps in clearly defining the project scope, estimating resources and time, and assigning responsibilities.
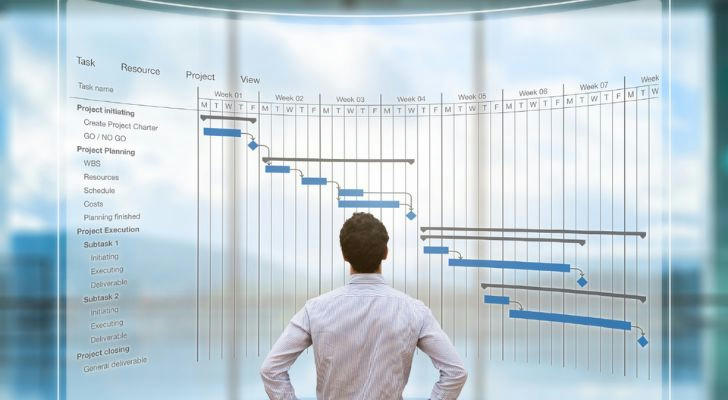
B. Gantt Charts
Gantt charts are visual representations of the project schedule. They display the start and end dates of tasks, their dependencies, and the overall project timeline. By using a Gantt chart, project managers can easily see how tasks are related and identify potential bottlenecks or delays.
For instance, if one task depends on the completion of another, it will be clearly shown in the chart. This allows managers to adjust the schedule accordingly and ensure that the project stays on track.
C. Critical Path Method (CPM)
The CPM is used to determine the longest sequence of dependent tasks in a project, known as the critical path. The tasks on the critical path have no slack time, meaning that any delay in these tasks will directly impact the project's completion date.
By identifying the critical path, project managers can focus their attention on the most crucial tasks and allocate resources accordingly to avoid delays.
II. Execution Tools and Techniques
A. Project Management Software
There are numerous project management software available today, such as Microsoft Project, Jira, and Trello. These tools help in managing project tasks, resources, schedules, and communications. They provide features like task assignment, progress tracking, and document sharing, enabling teams to collaborate effectively.
For example, in a marketing campaign project, team members can use project management software to update their task progress, share marketing materials, and communicate with each other.
B. Agile Methodologies
Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, emphasize iterative development and continuous improvement. In an Agile project, the work is divided into short sprints or iterations, and the team regularly reviews and adjusts the plan based on feedback.
This approach allows for greater flexibility and adaptability, especially in projects where requirements may change frequently. For instance, in a mobile app development project, the team can quickly respond to user feedback and make changes to the app during each sprint.

III. Monitoring and Control Tools and Techniques
A. Earned Value Management (EVM)
EVM is a technique used to measure project performance by comparing the planned value, earned value, and actual cost. The earned value represents the value of the work completed, while the planned value is the budgeted value for the work scheduled to be completed. By analyzing these values, project managers can determine whether the project is on schedule, within budget, and meeting its performance objectives. If there are variances, corrective actions can be taken promptly.
B. Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential risks that could impact the project. This includes developing risk response plans and monitoring risks throughout the project lifecycle. For example, in a construction project, risks such as weather delays, material shortages, and labor strikes need to be identified and managed. By having contingency plans in place, project managers can minimize the impact of these risks on the project.
Conclusion
The tools and techniques of project management are essential for the successful delivery of projects. By effectively using planning tools like WBS and Gantt charts, execution tools such as project management software and Agile methodologies, and monitoring and control tools like EVM and risk management, project managers can ensure that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of stakeholders.
